官方链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。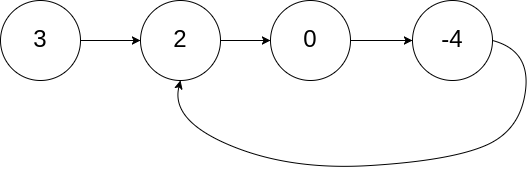
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。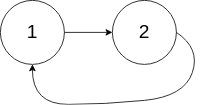
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
思路
- 暴力解法
- set
- 快慢指针
解法一 暴力解法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
for i in range(10000):
head = head.next
if not head:
return False
return True
解法二 set
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return false;
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) return true;
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
解法三 快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
解法四
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return false;
while (head != null) {
if (head == head.next) {
return true;
}
if (head.next != null) {
head.next = head.next.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}